운동하는 개발자/알고리즘, 코딩테스트
Beakjoon] DFS와 BFS (백준 1260 코테) - 탐색
우용현
2023. 12. 4. 22:34
728x90
🅰️문제주소 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1260
1260번: DFS와 BFS
첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000), 간선의 개수 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 10,000), 탐색을 시작할 정점의 번호 V가 주어진다. 다음 M개의 줄에는 간선이 연결하는 두 정점의 번호가 주어진다. 어떤 두 정점 사
www.acmicpc.net
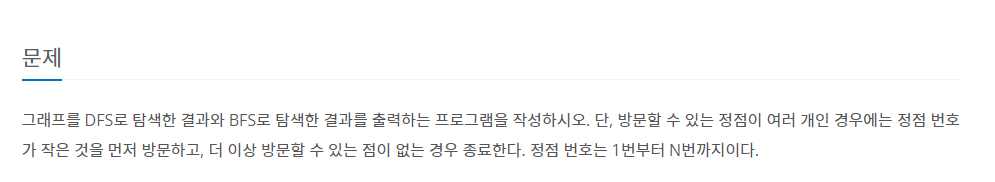
🚩문제
🪡풀이
- DFS와 BFS의 기본적인 구현. 탐색이 끊긴다던가 특정 depth의 값을 구하는 것이 아니므로 특별한 조건 없이 구현하면 된다.
주의할 점은 방문할 수 있는 정점이 여러개면 번호가 작은 것부터 방문하게 해야 한다는 것인데 이는 정렬을 통해 다른 조건을 줄 필요 없이 간단하게 해결된다.
☕코드는 아래 숨김
더보기
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
std::vector<bool> visited;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> map;
std::string result;
int N, M;
void DFS(int num) {
std::cout << num << " ";
visited[num] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < map[num].size(); ++i) {
if (visited[map[num][i]] == false)
DFS(map[num][i]);
}
return;
}
void BFS(int num) {
std::queue<int> myQ;
myQ.push(num);
visited[num] = true;
while (!myQ.empty()) {
int now_node = myQ.front();
myQ.pop();
std::cout << now_node << ' ';
for (int i : map[now_node]) {
if (visited[i] == false) {
visited[i] = true;
myQ.push(i);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(NULL);
std::cout.tie(NULL);
int V;
std::cin >> N >> M >> V;
visited.resize(N+1, false);
map.resize(N+1);
int f, b;
for (int i = 1; i <= M; ++i) {
std::cin >> f >> b;
map[f].push_back(b);
map[b].push_back(f);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
std::sort(map[i].begin(), map[i].end());
}
DFS(V);
std::cout << "\n";
result = "";
visited.resize(0);
visited.resize(N+1, false);
BFS(V);
}
💡알게 된 것
- BFS에 대해 이론적으로만 알고 있었으나 실제 C++에서 Queue를 사용하여 구현해봄.
- 이차원벡터의 sort 사용해 봄
728x90